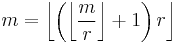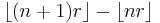Beatty sequence
In mathematics, a Beatty sequence (or homogeneous Beatty sequence) is the sequence of integers found by taking the floor of the positive multiples of a positive irrational number. Beatty sequences are named after Samuel Beatty, who wrote about them in 1926.
Rayleigh's theorem, named after Lord Rayleigh, states that the complement of a Beatty sequence, consisting of the positive integers that are not in the sequence, is itself a Beatty sequence generated by a different irrational number.
Beatty sequences can also be used to generate Sturmian words.
Contents |
Definition
A positive irrational number 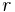 generates the Beatty sequence
generates the Beatty sequence
If 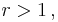 then
then 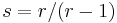 is also a positive irrational number. They naturally satisfy
is also a positive irrational number. They naturally satisfy
and the sequences
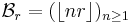 and
and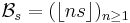
form a pair of complementary Beatty sequences.
A more general non-homogeneous Beatty sequence takes the form
where 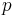 is a real number. For
is a real number. For 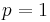 , the complementary non-homogeneous Beatty sequences can be found by making
, the complementary non-homogeneous Beatty sequences can be found by making 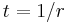 so that
so that
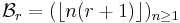 and
and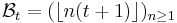
form a pair of complementary Beatty sequences. For other values of 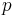 the procedure for finding complementary sequences is not as straightforward.
the procedure for finding complementary sequences is not as straightforward.
Examples
For r = the golden mean, we have s = r + 1. In this case, the sequence 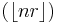 , known as the lower Wythoff sequence, is
, known as the lower Wythoff sequence, is
and the complementary sequence 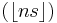 , the upper Wythoff sequence, is
, the upper Wythoff sequence, is
- 2, 5, 7, 10, 13, 15, 18, 20, 23, 26, 28, 31, 34, 36, 39, 41, 44, 47, ... (sequence A001950 in OEIS).
These sequences define the optimal strategy for Wythoff's game.
As another example, for r = √2, we have s = 2 + √2. In this case, the sequences are
- 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18, 19, 21, 22, 24, ... (sequence A001951 in OEIS) and
- 3, 6, 10, 13, 17, 20, 23, 27, 30, 34, 37, 40, 44, 47, 51, 54, 58, ... (sequence A001952 in OEIS).
Notice that any number in the first sequence is lacking in the second, and vice versa.
History
Beatty sequences got their name from the problem posed in the American Mathematical Monthly by Samuel Beatty in 1926.[1][2] It is probably one of the most often cited problems ever posed in the Monthly. However, even earlier, in 1894 such sequences were briefly mentioned by John W. Strutt (3rd Baron Rayleigh) in the second edition of his book The Theory of Sound.[3]
Rayleigh theorem
The Rayleigh theorem (also known as Beatty's theorem) states that given an irrational number 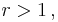 there exists
there exists 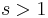 so that the Beatty sequences
so that the Beatty sequences 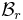 and
and 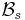 partition the set of positive integers: each positive integer belongs to exactly one of the two sequences.[3]
partition the set of positive integers: each positive integer belongs to exactly one of the two sequences.[3]
First proof
Given 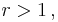 let
let 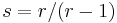 . We must show that every positive integer lies in one and only one of the two sequences
. We must show that every positive integer lies in one and only one of the two sequences 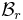 and
and 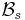 . We shall do so by considering the ordinal positions occupied by all the fractions j/r and k/s when they are jointly listed in nondecreasing order for positive integers j and k.
. We shall do so by considering the ordinal positions occupied by all the fractions j/r and k/s when they are jointly listed in nondecreasing order for positive integers j and k.
To see that no two of the numbers can occupy the same position (as a single number), suppose to the contrary that  for some j and k. Then r/s = j/k, a rational number, but also,
for some j and k. Then r/s = j/k, a rational number, but also, 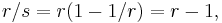 not a rational number. Therefore no two of the numbers occupy the same position.
not a rational number. Therefore no two of the numbers occupy the same position.
For any j/r, there are j numbers i/r ≤ j/r and 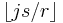 numbers
numbers 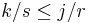 , so that the position of
, so that the position of 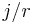 in the list is
in the list is 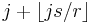 . The equation
. The equation 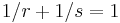 implies
implies
Likewise, the position of k/s in the list is 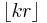 .
.
Conclusion: every positive integer (that is, every position in the list) is of the form 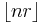 or of the form
or of the form 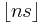 , but not both. The converse statement is also true: if p and q are two real numbers such that every positive integer occurs precisely once in the above list, then p and q are irrational and the sum of their reciprocals is 1.
, but not both. The converse statement is also true: if p and q are two real numbers such that every positive integer occurs precisely once in the above list, then p and q are irrational and the sum of their reciprocals is 1.
Second proof
Collisions: Suppose that, contrary to the theorem, there are integers j > 0 and k and m such that
This is equivalent to the inequalities
For non-zero j, the irrationality of r and s is incompatible with equality, so
which lead to
Adding these together and using the hypothesis, we get
which is impossible (one cannot have an integer between two adjacent integers). Thus the supposition must be false.
Anti-collisions: Suppose that, contrary to the theorem, there are integers j > 0 and k and m such that
Since j + 1 is non-zero and r and s are irrational, we can exclude equality, so
Then we get
Adding corresponding inequalities, we get
which is also impossible. Thus the supposition is false.
Properties
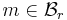 if and only
if and only
-
- where
![[x]_1](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/979b02ef8f2412786c8d3e2ea1028d10.png) denotes
denotes 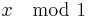 or the fractional part of
or the fractional part of  i.e.,
i.e., ![[x]_1 = x - \lfloor x \rfloor](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/8cd11a47a964a75a5320b4f4fa7ac9ff.png) . Furthermore, if
. Furthermore, if 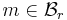
- Proof:
![m = \left\lfloor \frac{m}{r} \right\rfloor r %2B \left[ \frac{m}{r} \right]_1 r = \left( \left\lfloor \frac{m}{r}\right\rfloor %2B 1 \right)r - \left( 1 - \left[ \frac{m}{r} \right]_1 \right)r](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/d175a16f7592116b5a1101be2de3345d.png)
- If
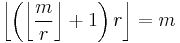 , then
, then ![\left\lfloor \left( \frac{m}{r} - \left[ \frac{m}{r} \right]_1 %2B 1\right) r \right\rfloor = m](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/88da0e1aa35856fa6aa8d41aa40d0c31.png)
- Or,
![\left\lfloor m %2B \left(1 - \left[ \frac{m}{r} \right]_1 \right)r \right\rfloor = m](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/da4e8bcfa1c29a8c12087fa1e78a0d8f.png) and thus,
and thus, ![0 \leq \left( 1 - \left[ \frac{m}{r} \right]_1 \right)r < 1](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/844f266b7404ee5b1ecdf0684c6dc162.png) which is the given condition rearranged.
which is the given condition rearranged.
Relation with Sturmian sequences
The first difference
of the Beatty sequence associated to the irrational number 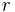 is a characteristic Sturmian word over the alphabet
is a characteristic Sturmian word over the alphabet  .
.
Generalizations
The Lambek–Moser theorem generalizes the Rayleigh theorem and shows that more general pairs of sequences defined from an integer function and its inverse have the same property of partitioning the integers.
References
- ^ Beatty, Samuel (1926). "Problem 3173". American Mathematical Monthly 33 (3): 159. doi:10.2307/2300153.
- ^ S. Beatty, A. Ostrowski, J. Hyslop, A. C. Aitken (1927). "Solutions to Problem 3173". American Mathematical Monthly 34 (3): 159–160. doi:10.2307/2298716. JSTOR 2298716.
- ^ a b John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh (1894). The Theory of Sound. 1 (Second ed.). Macmillan. p. 123. http://books.google.com/books?id=EGQSAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA123.
- Holshouser, Arthur; Reiter, Harold (2001). "A generalization of Beatty's Theorem". Southwest Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics 2: 24–29. http://www.math.uncc.edu/preprint/2002/2002_17.pdf.
- Stolarsky, Kenneth (1976). "Beatty sequences, continued fractions, and certain shift operators". Canadian Mathematical Bulletin 19 (4): 473–482. doi:10.4153/CMB-1976-071-6. MR0444558. Includes many references.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Beatty Sequence" from MathWorld.
- Alexander Bogomolny, Beatty Sequences, Cut-the-knot
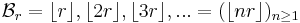
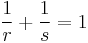
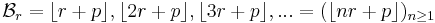
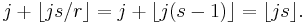
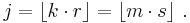
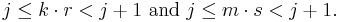
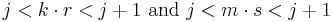
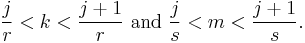
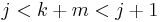
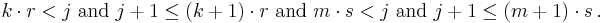
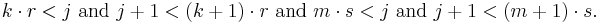
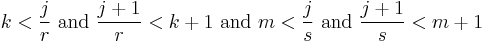
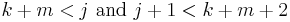
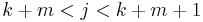
![0 \leq 1 - \frac{1}{r} \leq \left[ \frac{m}{r} \right]_1](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/af44eab6d19f4e182f1e778043e82ed7.png)